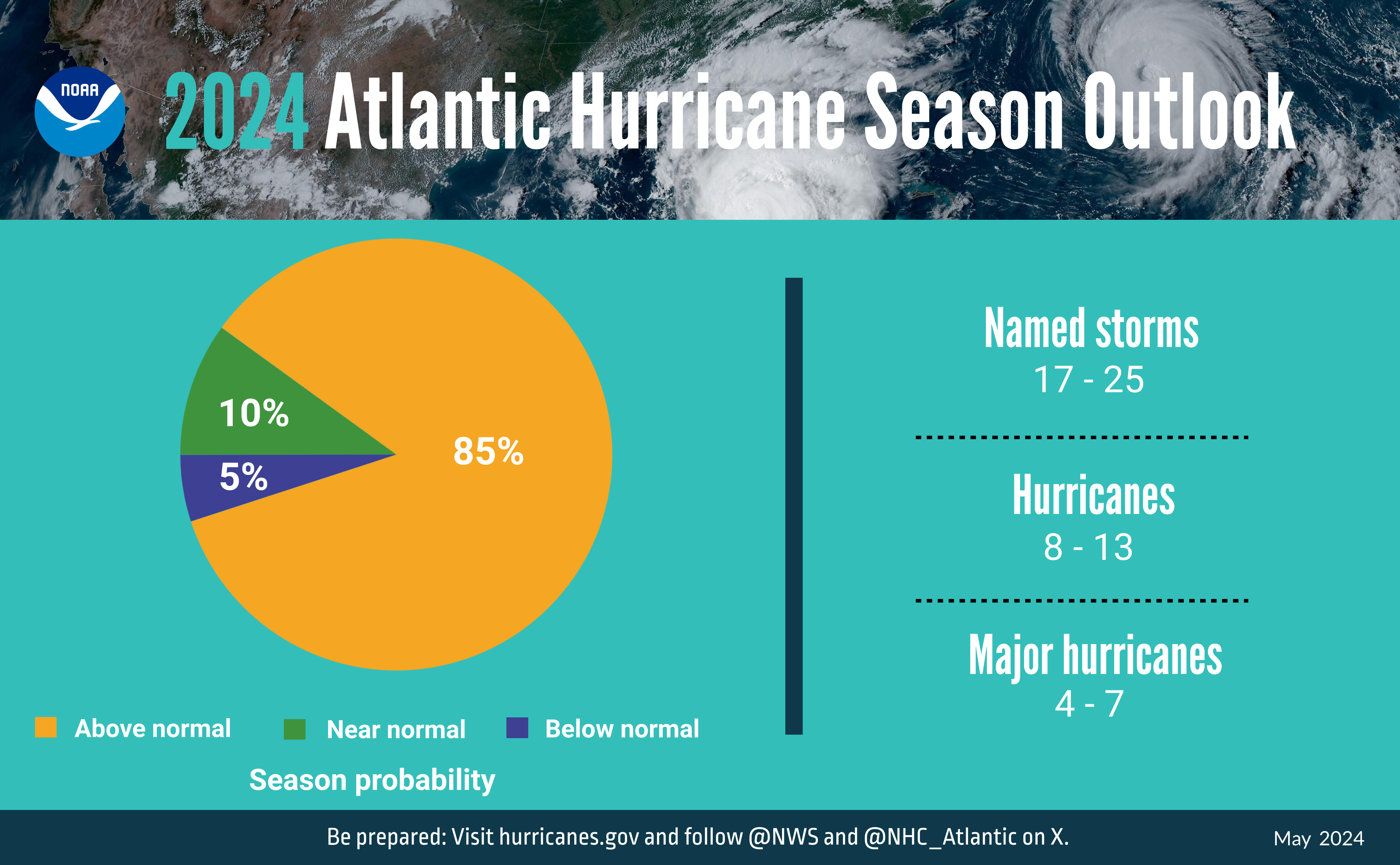
NOAA National Weather Service forecasters at the Climate Prediction Center predict above-normal hurricane activity in the Atlantic basin this year. NOAA’s outlook for the 2024 Atlantic hurricane season, which spans from June 1 to November 30, predicts an 85% chance of an above-normal season, a 10% chance of a near-normal season and a 5% chance of a below-normal season.
NOAA is forecasting a range of 17 to 25 total named storms (winds of 39 mph or higher). Of those, 8 to 13 are forecast to become hurricanes (winds of 74 mph or higher), including 4 to 7 major hurricanes (category 3, 4 or 5; with winds of 111 mph or higher). Forecasters have a 70% confidence in these ranges.
The upcoming Atlantic hurricane season is expected to have above-normal activity due to a confluence of factors, including near-record warm ocean temperatures in the Atlantic Ocean, development of La Nina conditions in the Pacific, reduced Atlantic trade winds and less wind shear, all of which tend to favor tropical storm formation.
“With another active hurricane season approaching, NOAA’s commitment to keeping every American informed with life-saving information is unwavering,” said NOAA Administrator Rick Spinrad, Ph.D. “AI-enabled language translations and a new depiction of inland wind threats in the forecast cone are just two examples of the proactive steps our agency is taking to meet our mission of saving lives and protecting property.”
"Severe weather and emergencies can happen at any moment, which is why individuals and communities need to be prepared today," said FEMA Deputy Administrator Erik A. Hooks. "Already, we are seeing storms move across the country that can bring additional hazards like tornadoes, flooding and hail. Taking a proactive approach to our increasingly challenging climate landscape today can make a difference in how people can recover tomorrow."

As one of the strongest El Ninos ever observed nears its end, NOAA scientists predict a quick transition to La Nina conditions, which are conducive to Atlantic hurricane activity because La Nina tends to lessen wind shear in the tropics. At the same time, abundant oceanic heat content in the tropical Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Sea creates more energy to fuel storm development.
This hurricane season also features the potential for an above-normal west African monsoon, which can produce African easterly waves that seed some of the strongest and longer-lived Atlantic storms. Finally, light trade winds allow hurricanes to grow in strength without the disruption of strong wind shear, and also minimize ocean cooling. Human-caused climate change is warming our ocean globally and in the Atlantic basin, and melting ice on land, leading to sea level rise, which increases the risk of storm surge. Sea level rise represents a clear human influence on the damage potential from a given hurricane.
Enhanced communications in store for 2024 season
NOAA will implement improvements to its forecast communications, decision support and storm recovery efforts this season. These include:
- The National Hurricane Center (NHC) will expand its offering of Spanish language text products to include all Public Advisories, the Tropical Cyclone Discussion, the Tropical Cyclone Update and Key Messages in the Atlantic basin.
- Beginning on or around August 15, NHC will start to issue an experimental version of the forecast cone graphic that includes a depiction of inland tropical storm and hurricane watches and warnings in effect for the continental U.S. Research indicates that the addition of inland watches and warnings to the cone graphic will help communicate inland hazards during tropical cyclone events without overcomplicating the current version of the graphic.
- This season, the NHC will be able to issue U.S. tropical cyclone watches and warnings with regular or intermediate public advisories. This means that if updates to watches and warnings for storm surge or winds are needed, the NHC will be able to notify the public in an intermediate advisory instead of having to wait for the next full advisory issued every 6 hours.
New tools for hurricane analysis and forecasting this year
- Two new forecast models developed by NOAA researchers will go into operation this season: The Modular Ocean Model or MOM6 will be added to the Hurricane Analysis and Forecast System to improve the representation of the key role the ocean plays in driving hurricane intensity. Another model, SDCON, will predict the probability of tropical cyclone rapid intensification.
- NOAA’s new generation of Flood Inundation Mapping, made possible through President Biden’s Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, will provide information to emergency and water managers to prepare and respond to potential flooding and help local officials better prepare to protect people and infrastructure.
- NOAA’s Weather Prediction Center, in partnership with the NHC, will issue an experimental rainfall graphic for the Caribbean and Central America during the 2024 hurricane season. This graphic provides forecast rainfall totals associated with a tropical cyclone or disturbance for a specified time period.
System upgrades in operation
NOAA will upgrade its observing systems critical in understanding and forecasting hurricanes. These projects will provide more observations of the ocean and atmosphere in the Caribbean, the Gulf of Mexico, on the U.S. East Coast and in the tropical Atlantic.
- NOAA’s National Data Buoy Center recently upgraded many coastal weather buoys in the tropical western Atlantic and Caribbean to include time of occurrence and measurements of one-minute wind speed and direction, 5-second peak wind gust and direction and lowest 1-minute barometric pressure to support tropical cyclone forecasting.
- New this year, NOAA will gather additional observations using Directional Wave Spectra Drifters (DWSDs), deployed from the NOAA P-3 hurricane hunter aircraft and in the vicinity of Saildrones, uncrewed surface vehicles which will be deployed at the start of the hurricane season, providing one-minute data in real time. 11-12 Saildrones are planned for deployment in 2024.
- Starting in June, dozens of observational underwater gliders are planned to deploy in waters off the Caribbean, Gulf of Mexico and the eastern U.S. coast. Additionally, a new lightweight dropsonde called Streamsonde will be deployed into developing tropical storms, collecting multiple real-time observations to collect valuable wind data.
- The CHAOS (Coordinated Hurricane Atmosphere-Ocean Sampling) research experiment aims to improve the understanding of air-sea interactions, providing sustained monitoring of key ocean features.
About NOAA seasonal outlooks
NOAA’s outlook is for overall seasonal activity and is not a landfall forecast. In addition to the Atlantic seasonal outlook, NOAA also issues seasonal hurricane outlooks for the eastern Pacific, central Pacific and western north Pacific hurricane basins.
NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center will update the 2024 Atlantic seasonal outlook in early August, prior to the historical peak of the season.
Climate, weather, and water affect all life on our ocean planet. NOAA’s mission is to understand and predict our changing environment, from the deep sea to outer space, and to manage and conserve America’s coastal and marine resources.




